For years now, Google has been on the forefront of making internet a better place for its billions of users. In that time, Google has come up with several innovations, products and services in a bid to make finding information online an easy and lightning fast experience. But Google has always been like a one-eyed archer perched on a horseback trying to hit a moving hummingbird while it rains heavily.
Google’s innovations have often missed their mark as much as they have hit the target if not more. One of the Google arrow to have gone haywire is Google Authorship.
What Is Google Authorship?
Google Authorship was primarily Google’s way to allow the authors of content to identify themselves for display purposes. Google speculated that having an authoritative figure next to a link to a piece of information helped provide credibility to the content.
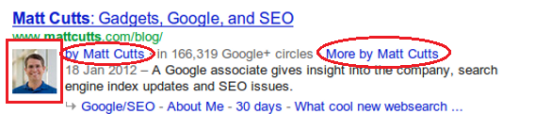
It was implemented by making use of the “markup” tag within the code of the web page. Later, with the introduction of Google+, the concept of identifying and displaying the author was made even more close-knit. Google Authorship rewarded its users by having author names and images appear next to their stories.
Why Google Pulled The Plug To Authorship Markup on SERP?
And then in the Fall of 2014, it all ended.
Google took the plug off of Google Authorship citing underachievement of its intended goals. Time and again, Google has shown that nothing it makes comes with the guarantee to last forever. A stark remainder of this hit content creators and SEO industry when Google announced that all photos would be removed from global search with only bylines remaining visible in the search results.
According to Google’s John Mueller, the primary reason behind dropping Google Authorship from the Search Bandwagon was its low adoption rate and low value to the users. Participation in authorship markup by content creators was spotty at best, and almost non-existent in many verticals, especially in case of users who were not very tech-savvy.
How Google Authorship Backfired & Died
In order to move over this hurdle, Google decided to auto-attribute authorship where no byline could be found.
However, this strategy backfired spectacularly for Google when several articles were misattributed to people who never wrote them and in one case, was dead for 28 years before he was attributed as the author of a New York Times article.
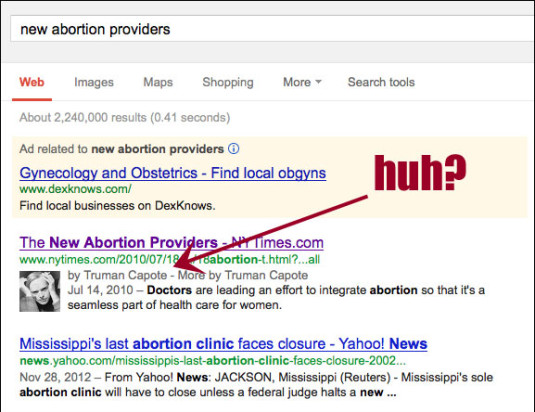
After collecting three years of data, it was also observed that there was no significant improvement in the click behavior of the users on the search results pages. Google’s data showed users were not getting sufficient value from Authorship snippets.
It has largely been believed that the main reason behind this anomaly was that over time, users became used to seeing the mugshot of authors next to search results and thus did not feel compelled enough to click through them.
Rise Of Author Rank – Another Phoenix From Google’s Yard?
Amid the murmurs of the untimely demise of Google Authorship rose the concept of Author Rank. Google has always shown deep interest in assigning authors to the online content in order to increase the credibility of the content as well as to enable the users to access information from authoritative sources.
Baptized by Google as Agent Rank, the SEO community renamed it as Author Rank as this new concept purportedly altered the rankings of a content piece based on Google’s knowledge of the content’s author.
With the death of Google Authorship, it was speculated that Author Rank was also going to be a thing of the past, a relic of Google’s habit of introducing new concepts and then discarding them because they didn’t fare as well as previously thought.
However, Google has always been as secretive about Author Rank as they were openly critical about Google Authorship.
Matt Cutts, the famous head of webspam at Google, said of Author Rank “it does comes into play in some ways. For example, in-depth articles use that data, I’m pretty sure.”
Google’s Author Rank & SEO Rankings – Whats The Link?
There has been a recent resurgence in rumors that an improved version of Agent Rank is returning to Google Search Results. This is because recently Google has been granted a patent that appears to be dealing with profile images and snippets of “prominent people in response to specific queries, which look like they are related to the topic of a query, rather than just a profile image. It has been rumored that Google has modified and improved the Author Rank.
This appears to be a more refined form of the Author Rank as it also gives an explanation as to why someone might be displayed as having some level of expertise in response to a query that you perform.
However, the SEO community has shown controlled information about the “new” Author Rank as it has been hinted by Google that as of now, it contributes in a very limited fashion to Google’s ranking factors.
Still, it is worth looking carefully at this patent, and seeing if it is actually a followup to Agent Rank or Author Rank as well as how much effect it will have on the eventual search results.

